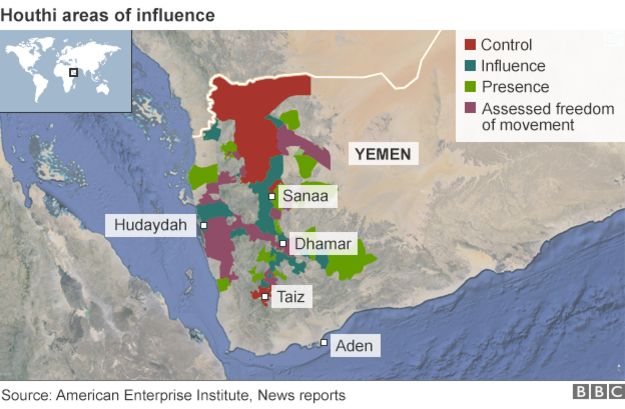
Yemen has descended into conflicts between several different groups, pushing the country "to the edge of civil war"
The main fight is between -
- forces loyal to the beleaguered President Abdrabbuh Mansour Hadi, and
- those allied to Zaidi Shia rebels known as Houthis
President Hadi, who is recognised as Yemen's legitimate leader by the international community, managed to escape to Aden, which he declared the de facto capital
Who are the Houthis?
The Houthis take their name from Hussein Badr al-Din al-Houthi. He led the group's first uprising in 2004 in an effort to win greater autonomy for their heartland of Saada province, and also to protect Zaidi religious and cultural traditions from perceived encroachment by Sunni Islamists.
The conflict between the Houthis and the elected government is also seen as part of a regional power struggle between Shia-ruled Iran and Sunni-ruled Saudi Arabia, which shares a long border with Yemen.
Yemen's security forces have split loyalties, with some units backing Hadi, and others the Houthis and Hadi's predecessor Ali Abdullah Saleh, who has remained politically influential
Both President Hadi and the Houthis are opposed by al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP), which has staged numerous deadly attacks from its strongholds in the south and south-east
The situation is further complicated by the emergence in late 2014 of a Yemen affiliate of the jihadist group Islamic State, which seeks to eclipse AQAP and claims it carried out a series of suicide bombings in Sanaa in March 2015
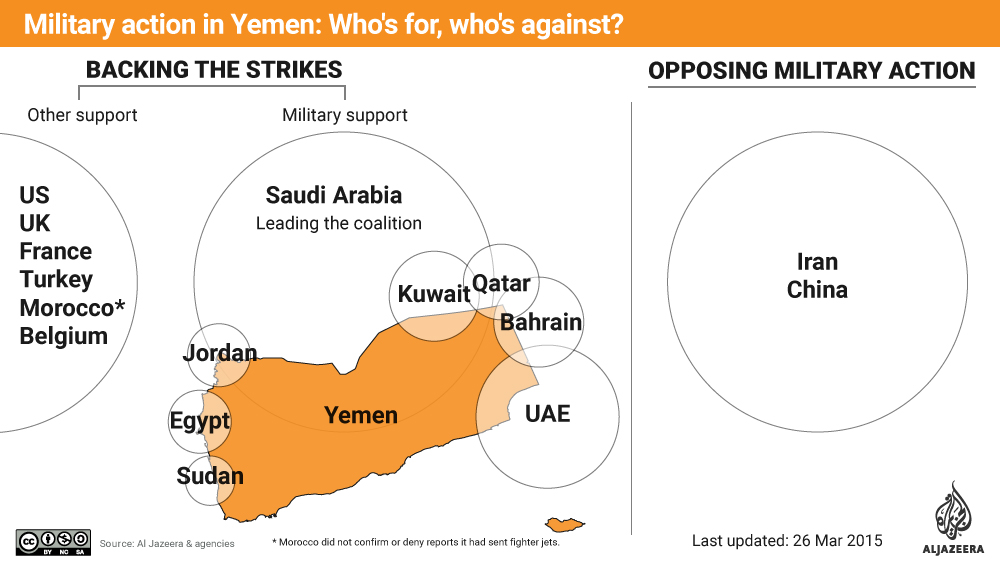
Saudi Arabia leads air strikes against Iranian-backed Houthi rebels
The coalition comprises five Gulf Arab states and Jordan, Egypt, Morocco, Pakistan and Sudan.
No comments:
Post a Comment