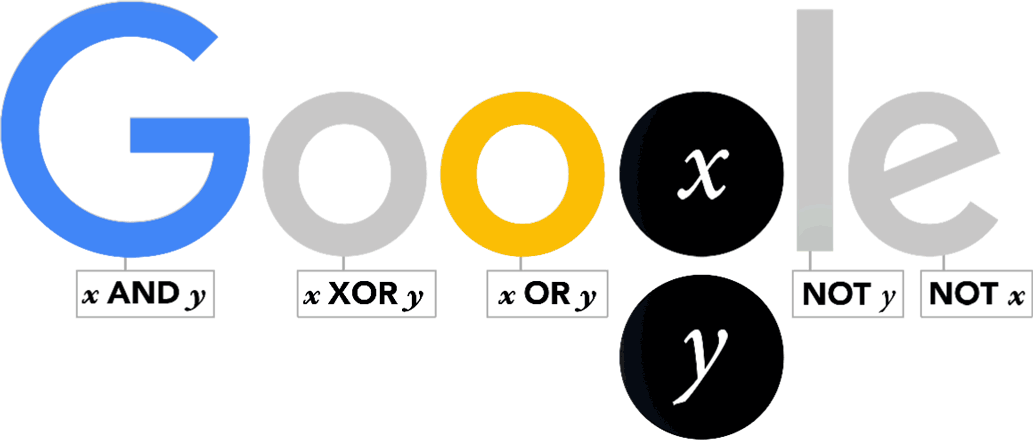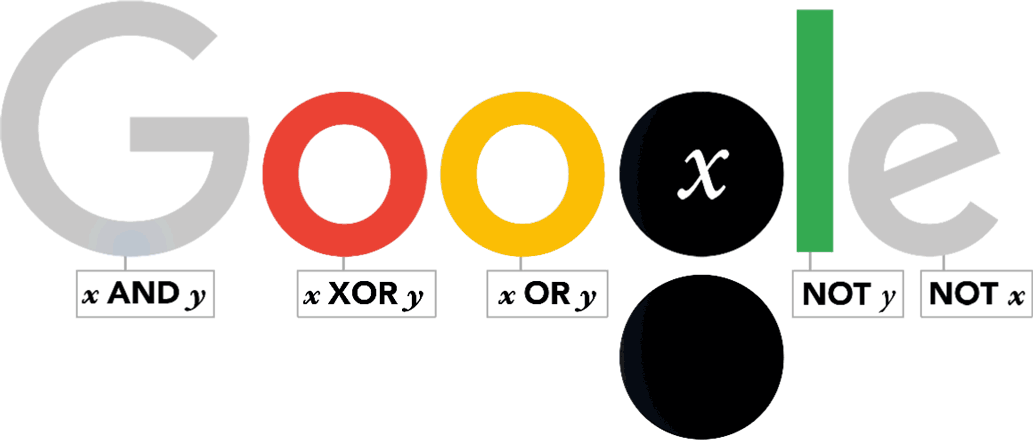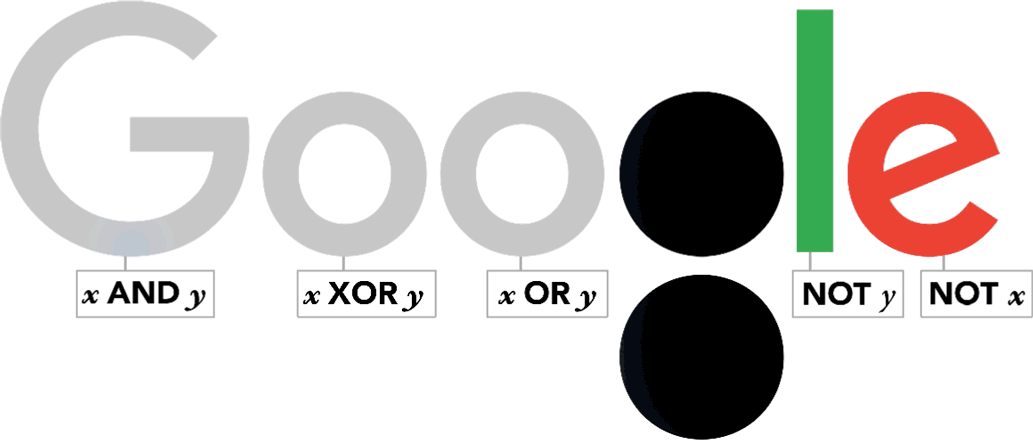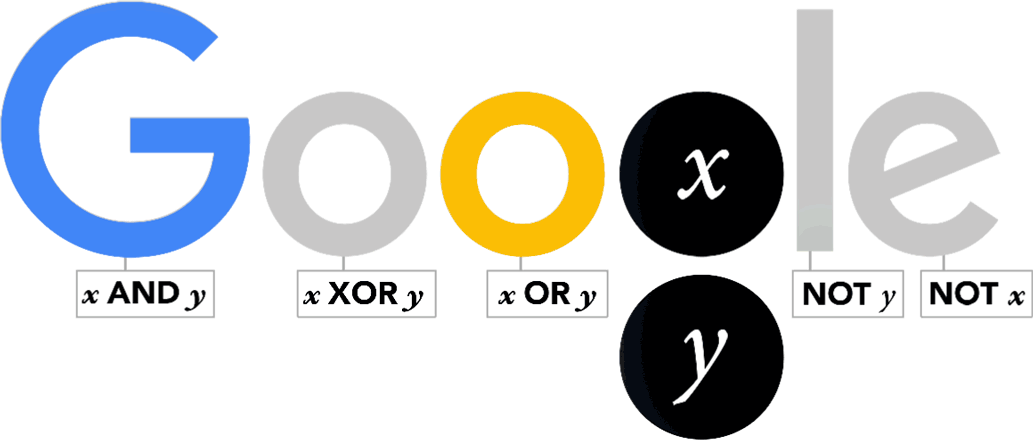
Boole work, commonly referred to as Boolean
algebra, went on to influence binary systems used in electrical circuits
and computers.
The Doodle shows the '' logic gates'' derived from Boolean theories often used in modern computing.
Boole’s talents didn’t lie solely with
mathematics, however. Born in Lincolnshire in the U.K., Boole ended his
formal education at 14 but still managed to teach himself poetry and a
slew of languages. By the age of 20 he had even opened up his own
school.
His scientific successes
came later — he was the first pure mathematician to receive the Gold
Medal for Mathematics by the Royal Society in 1844, only three years
after his first publication on the subject.
He then became the first mathematics professor at Ireland’s University College Cork, then known as Queen’s College Cork, in 1849 — a position which he retained for the rest of his life. He wrote his most famous work, An Investigation of the Laws of Thought, there in 1854
Boole fell ill with pneumonia and passed away in Cork in 1864 at the age of 49. He was survived by five daughters, many of whom ended up making significant contributions to maths and sciences themselves.
No comments:
Post a Comment