
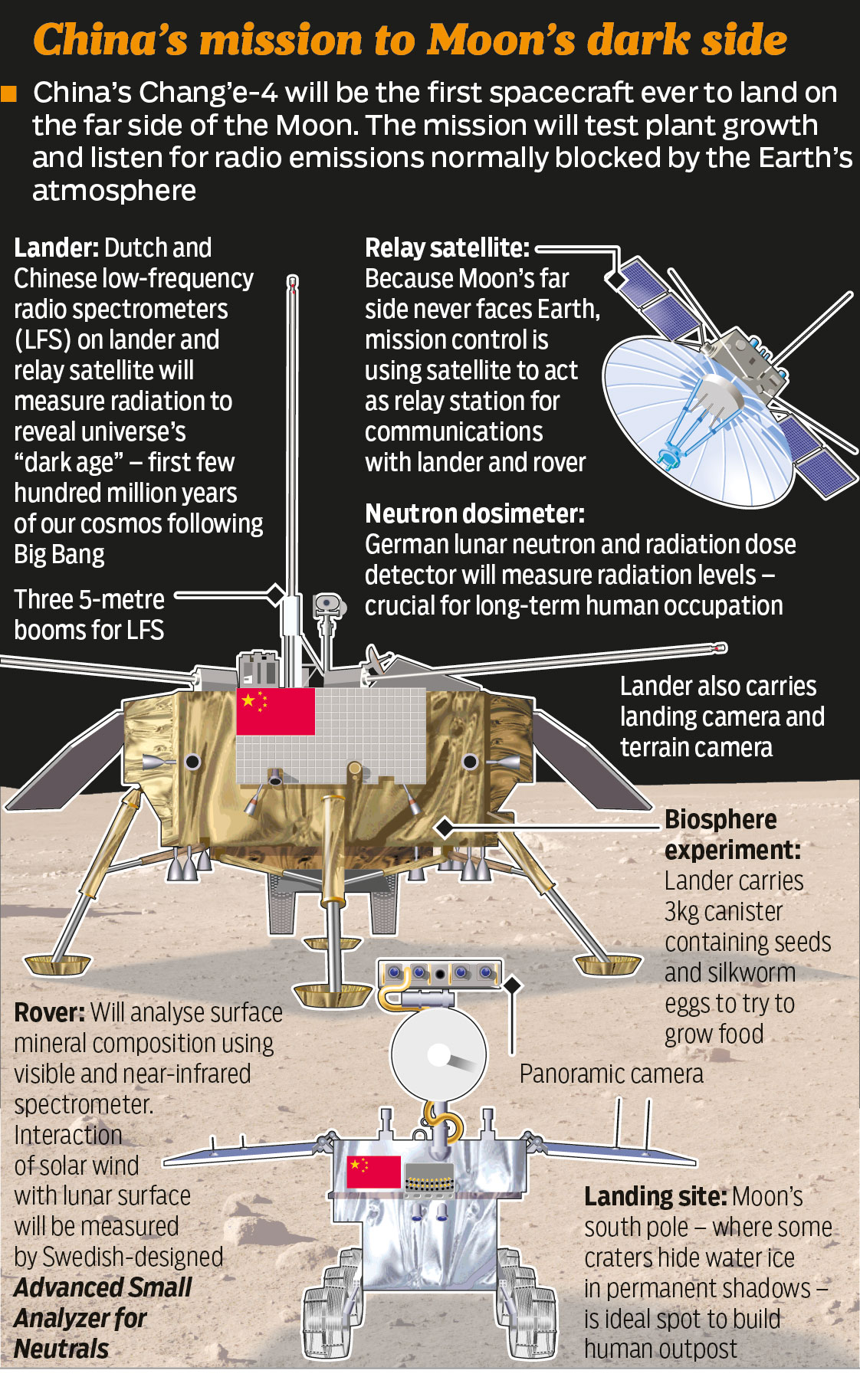
China says it has successfully landed a robotic spacecraft on the far side of the Moon, the first ever such attempt and landing.

The
Chang'e-4 lunar rover is lifted into space from the Xichang launch
centre in Xichang in China's southwestern Sichuan province on Dec 07,2018

At 10:26 Beijing time (02:26 GMT), the unmanned Chang'e-4 probe touched down in the South Pole-Aitken Basin, state media said.
It is carrying instruments to characterise the region's geology, as well as a biological experiment.
State media called the landing "a major milestone in space exploration"
While past missions have been to the Earth-facing side, this is the first time a craft has landed on the unexplored far side.
The probe has sent some first pictures from the surface.
With no direct communications link possible, all pictures and data are first sent to a separate satellite and then relayed from there to earth.

A
never-before-seen 'close range' image taken by the Chinese
spacecraft Chang'e-4 of the surface of the far side of the moon. It
appears to take on a reddish hue in some of the images released by
China, seemingly an effect of the lights used by the probe

A TIMELINE OF HOW CHINA REACHED THE FAR SIDE OF THE MOON
October
24 2007 - China launches Chang'e-1, an unmanned satellite, into space
where it remains operational for more than a year.
October
1 2010 - China launches Chang'e-2. This was part of the first phase of
the Chinese moon programme. It was in a 100-km-high lunar orbit to
gather data for the upcoming Chang'e-3 mission.
September 29, 2011 - China launched Tiangong 1.
September 15 2013 - A second space lab, Tiangong 2, is launched.
December 1 2013 - Chang'e-3 launched.
December
14 2013 - Chang'e-3, a 2,600 lb (1,200 kg) lunar probe landed on the
near side of the moon successfully. It became the first object to
soft-land on the Moon since Luna 24 in 1976.
April 1 2018 - Tiangong-1 crashed into Earth at 17,000 mph and lands in the ocean off the coast if Tahiti.
May
20 2018 - China launched a relay satellite named Queqiao which is
stationed in operational orbit about 40,000 miles beyond the moon. This
is designed to enable Chang'e-4 to communicate wit engineers back on
Earth.
December 7 2018 - Chinese space agency announces it has laumched the Chang'e-4 probe into space.
December 12 2018 - Retrorockets on the probe fired to stabilise the spacecraft and slow it down.
December 31 2018 - The probe prepared for the first-ever soft landing on the far side of the moon.
No comments:
Post a Comment